Dr Johanna Feary
Jo Feary speaks at annual FOM conference 2026
Thu, 15 Jan 2026

Dr Jo Feary discussed occupational asthma and the rising risks of accelerated silicosis from engineered stone at the recent annual conference hosted by the Faculty of Occupational Medicine (FOM) for Occupational Medicine Resident and Portfolio Pathway doctors, titled "Occupational Health Horizons: Empowering Tomorrow’s Practitioners".
The conference was held on 15th January 2026 at the University of Warwick, UK.
Jo Feary speaks on podcast
Thu, 30 Oct 2025

Dr Jo Feary was interviewed for the Society of Occupational Medicine (SOM) podcast on an episode about silicosis due to artificial/engineered stone.
Listen on the following channels:
Read more about the SOM podcast on their website.
Jo Feary talks about artificial stone silicosis on BBC Morning Live
Tue, 13 May 2025

Dr Johanna Feary was recently featured on BBC Morning Live at Royal Brompton Hospital to talk about silicosis due to artificial stone, and advises those working with the material to get their lungs checked.
The feature also includes an interview with our patient Ryan, who spoke about how his silicosis diagnosis has affected his life. Nurse Tamanna Kabir was also featured performing spirometry with Ryan.
Watch the feature on BBC Morning Live online from 11mins and 22 secs.
Jo Feary talks about artificial stone silicosis on Channel 4 News
Mon, 28 Oct 2024
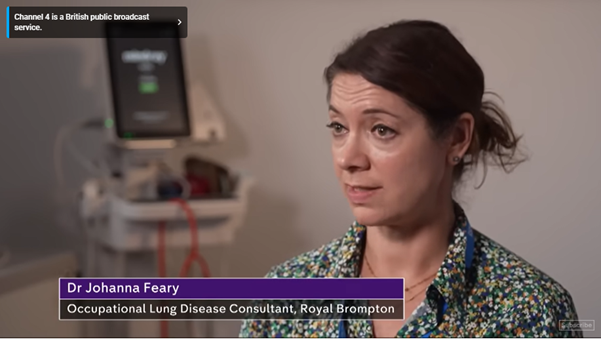
Dr Johanna Feary, Honorary Consultant in Occupational Lung Disease and Asthma, and patient Marek Marzec were recently interviewed by Channel 4 News to discuss the dangers of silicosis due to artificial stone. The piece was aired on Monday 28th October 2024 and you can watch it online here.
If you have ever worked with silica, stone dust, artificial stone or quartz and you are worried about silicosis, please email us now.
We see patients with suspected silicosis in our Occupational Lung Disease NHS clinic.
Laboratory animal allergy is preventable in modern research facilities
Mortality risk associated with occupational exposures in people with small airways obstruction
Background
Small airways obstruction (SAO) has been associated with occupational exposures. Whether exposure to harmful occupational agents impacts the survival of people with SAO is unknown. Our aim was to estimate the mortality risk associated with occupational exposures among people with SAO.
Methods
Occupational contributions to Interstitial Lung Disease
- Globally, coal workers pneumoconiosis, silicosis, and asbestosis remain the most important pneumoconioses.
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and asbestosis can be challenging to differentiate clinically, and there is clear evidence for an occupational contribution to IPF.
- Bacterial contamination of metal working fluid has recently emerged as an important cause of occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Occupational exposure to particulate matter and staff sickness absence on the London underground
The London Underground (LU) employs over 19,000 staff, some of whom are exposed to elevated concentrations of particulate matter (PM) within the network. This study quantified the occupational exposure of LU staff to subway PM and investigated the possible association with sickness absence (SA).
A job exposure matrix to quantify subway PM2.5 staff exposure was developed by undertaking measurement campaigns across the LU network. The association between exposure and SA was evaluated using zero-inflated mixed-effects negative binomial models.
Occupational exposures and small airway obstruction in the UK Biobank Cohort
Background
Small airways obstruction (SAO) is a key feature of both COPD and asthma, which have been associated with workplace exposures. Whether SAO, which may occur early in the development of obstructive lung disease and without symptoms, also associates with occupational exposures is unknown.
Methods
Occupational lung disease: what the general physician needs to know
Occupational exposures are a common and preventable cause of lung disease. About one in six cases of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma worldwide are related to work.
